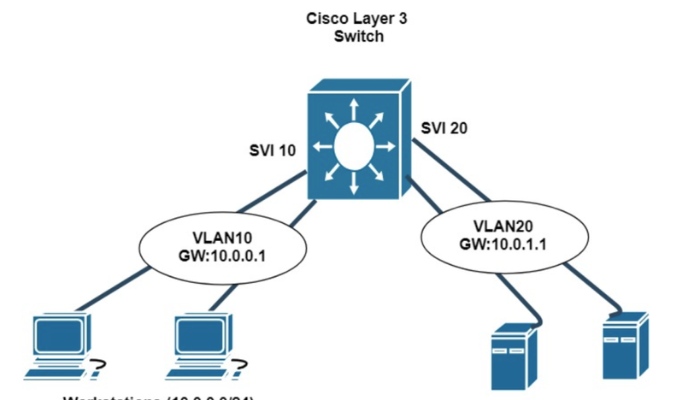
In modern networking, seamless communication across VLANs is essential. A Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) plays a critical role in enabling Layer 3 routing on Layer 2 switches. It allows devices in different VLANs to communicate without requiring an external router. Understanding SVIs is crucial for network administrators seeking to optimize network performance, simplify configurations, and improve security. In this guide, we will explore the fundamentals of SVI, its configuration, advantages, troubleshooting tips, and common FAQs.
What is a Switch Virtual Interface (SVI)?
A Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) is a logical interface on a switch that provides Layer 3 capabilities, enabling inter-VLAN routing without the need for an external router. Unlike physical interfaces, SVIs do not require dedicated hardware ports but instead operate as virtual interfaces assigned to VLANs.
Key Features of SVI:
- Provides Layer 3 IP routing within VLANs.
- Reduces reliance on external routers for inter-VLAN communication.
- Improves network efficiency and performance by decreasing traffic congestion.
- Supports network management features like security policies and access control.
When configured correctly, SVIs enhance network functionality by allowing devices within different VLANs to communicate efficiently, making them a fundamental component of enterprise networks.
How to Configure a Switch Virtual Interface (SVI)?
Setting up an SVI is a straightforward process involving VLAN creation, assigning an IP address,switch virtual interface and enabling routing. Below is a step-by-step guide to configuring an SVI on a Cisco switch.
Step 1: Create a VLAN
First, create a VLAN to which the SVI will be assigned.
Switch(config)# vlan 10
Switch(config-vlan)# name HR_VLAN
Switch(config-vlan)# exit
Step 2: Configure the SVI
Assign an IP address to the VLAN interface to enable Layer 3 connectivity.
Switch(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 3: Enable IP Routing (if necessary)
For inter-VLAN communication, enable IP routing on Layer 3 switches.
Switch(config)# ip routing
Step 4: Assign VLAN to Ports
Ensure switch ports are assigned to the correct VLAN.
Switch(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10
Once configured, the SVI facilitates communication across VLANs without the need for an external router.
Benefits of Using Switch Virtual Interfaces
Implementing SVI in a network infrastructure brings multiple advantages.switch virtual interface Here are some key benefits:
3.1 Enhanced Network Performance
SVIs reduce the need for external routing devices, minimizing latency and enhancing data transmission speeds. By keeping inter-VLAN communication within the switch, network congestion is significantly reduced.
3.2 Simplified Network Management
With SVIs, administrators can easily manage VLAN configurations and apply security policies directly within the switch. This centralization of control streamlines network management tasks.
3.3 Cost-Effective Solution
Since SVIs eliminate the need for additional routers for VLAN routing, organizations can reduce hardware costs while optimizing performance. This is particularly beneficial for enterprises with extensive VLAN structures.
3.4 Improved Security
Using Access Control Lists (ACLs) and firewall rules with SVIs allows for more granular control over traffic, ensuring secure communication between VLANs.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting SVIs
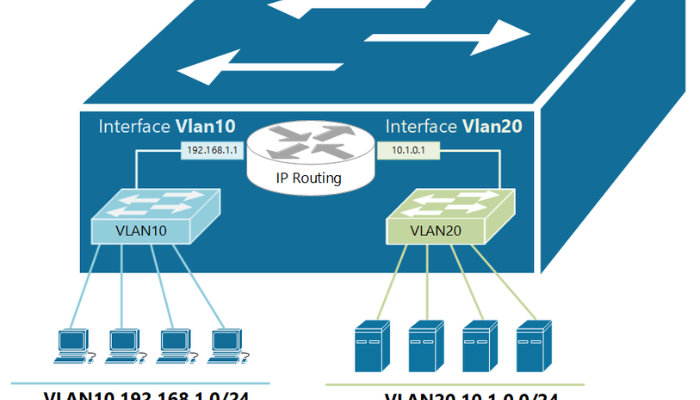
Despite their advantages,switch virtual interface SVIs may sometimes face connectivity issues. Below are common problems and their solutions:
4.1 SVI is Down or Unreachable
Possible Causes:
- The VLAN interface is shut down.
- No active ports are assigned to the VLAN.
- Incorrect subnet configuration.
Solution:
Switch# show ip interface brief
Switch(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Ensure at least one active port is associated with the VLAN.
4.2 Inter-VLAN Routing Not Working
Possible Causes:
- IP routing is not enabled.
- ACLs are blocking traffic between VLANs.
Solution: Enable IP routing and verify ACL settings:
Switch(config)# ip routing
Switch# show access-lists
Modify ACLs if necessary to permit traffic between VLANs.
4.3 High Latency or Slow Performance
Possible Causes:
- Network congestion due to excessive broadcasts.
- Improper VLAN design.
Solution:
- Implement VLAN trunking to optimize traffic flow.
- Use Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize critical traffic.
Best Practices for Implementing SVIs
To maximize the effectiveness of SVIs,switch virtual interface follow these best practices:
5.1 Proper VLAN Segmentation
Ensure VLANs are logically segmented based on departments or functions to minimize unnecessary traffic and enhance security.
5.2 Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Use network monitoring tools like SNMP and Syslog to track SVI performance and troubleshoot issues proactively.
5.3 Secure Configuration
Implement ACLs and security policies to restrict unauthorized access between VLANs. Consider using DHCP snooping and port security for added protection.
5.4 Backup Configuration
Regularly back up switch configurations using TFTP or network automation tools to prevent data loss in case of failures.
Conclusion
Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVI) play a vital role in modern network architectures, enabling efficient VLAN routing without external hardware. With proper configuration and best practices, SVIs enhance network performance, simplify management, and improve security. By understanding their implementation and troubleshooting methods, network administrators can optimize their infrastructure for seamless communication.
FAQs
- What is the purpose of an SVI?
SVIs enable Layer 3 routing on a Layer 2 switch,switch virtual interface allowing inter-VLAN communication without an external router. - Can an SVI be assigned to multiple VLANs?
No, an SVI is assigned to a single VLAN. - What is the default VLAN for an SVI?
By default, VLAN 1 is assigned an SVI, but it can be changed. - Do all switches support SVIs?
Only Layer 3-capable switches support SVIs for routing. - How many SVIs can a switch have?
The number varies by switch model but typically ranges from a few to hundreds switch virtual interface. - Can SVIs be used with DHCP?
Yes, SVIs can be configured as DHCP relay agents to forward requests. - How do I check active SVIs on a switch?
Use show ip interface brief to list active SVIs. - Do SVIs require an IP address?
Yes, an IP address must be assigned for Layer 3 functionality. - What is the role of ACLs with SVIs?
ACLs control traffic flow between VLANs using SVIs. - Why is my SVI showing as down?
Ensure the VLAN has active ports and the interface is not administratively shut down switch virtual interface.