SVI networking, or Switch Virtual Interface networking, is a crucial aspect of modern network design, allowing efficient communication between VLANs without relying on external routers. By leveraging SVIs, organizations can enhance network performance, simplify configurations, and improve security. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of SVI networking, its benefits, setup procedures, best practices, and troubleshooting techniques to optimize your network infrastructure.
Understanding SVI Networking: What It Is and How It Works
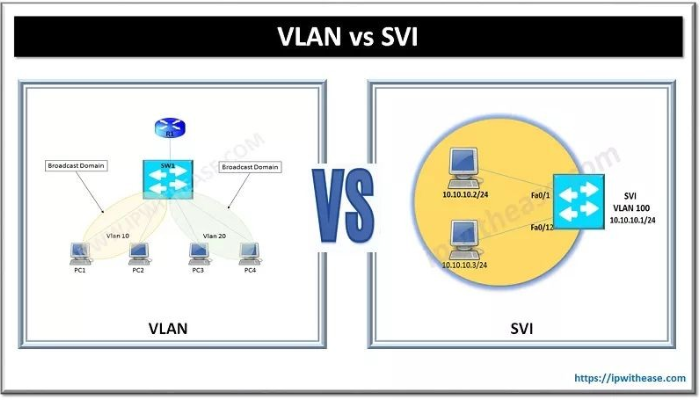
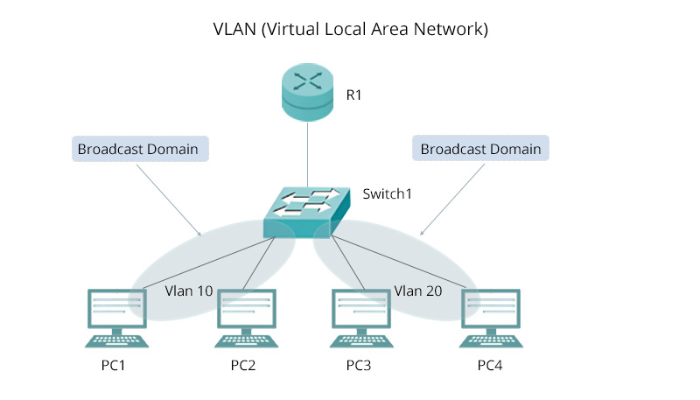
Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs) are logical interfaces configured on a Layer 3 switch to enable inter-VLAN routing. Unlike traditional VLANs that require an external router for communication, an SVI allows a switch to act as a router, reducing latency and improving efficiency.
SVIs work by assigning an IP address to a VLAN interface, allowing it to route traffic between different VLANs. This eliminates the need for a separate physical router and reduces network congestion. Enterprises that deploy SVI networking benefit from simplified management and enhanced performance.
Key Benefits of SVI Networking
Improved Network Performance
By handling inter-VLAN routing internally within the switch, SVIs reduce the need for traffic to traverse external routers, significantly decreasing latency and increasing data transfer speeds. This improvement is especially beneficial in high-traffic environments.
Simplified Configuration and Management
Configuring an SVI is much simpler than setting up an external router for VLAN routing. Network administrators can manage VLANs more efficiently and streamline configurations using a single switch rather than dealing with multiple networking devices.
How to Configure SVI Networking on a Cisco Switch
Step 1: Enable IP Routing on the Switch
Before configuring an SVI, ensure that IP routing is enabled on the switch. Use the following command in the CLI:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# ip routing
Step 2: Create and Configure the SVI
Assign an IP address to the VLAN interface using the following commands:
Switch(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
This command enables inter-VLAN communication for VLAN 10 by assigning it an IP address.
Best Practices for SVI Networking
Use Proper IP Addressing and Subnetting
To ensure efficient routing, assign logical IP address schemes to your VLANs.svi networking Proper subnetting helps in traffic segmentation and improves security.
Implement Security Measures
Since SVIs handle inter-VLAN traffic, it’s essential to secure them using ACLs (Access Control Lists) to restrict unauthorized access. Implementing VLAN access lists (VACLs) enhances security.
Optimize Load Balancing and Redundancy
To prevent network failures, configure multiple SVIs with load-balancing protocols like HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) to ensure high availability and reliability.
Troubleshooting Common SVI Networking Issues
SVI Not Responding to Pings
If an SVI is not responding, verify that the VLAN interface is up and running. Use:
Switch# show ip interface brief
Ensure that the VLAN is assigned to active switch ports.
Inter-VLAN Routing Not Working
Check whether IP routing is enabled on the switch. Without it, SVIs cannot route traffic between VLANs. Also, verify that the correct VLANs are assigned to switch ports.
Slow Network Performance
If network speeds are slower than expected, analyze traffic flow using network monitoring tools and optimize VLAN segmentation to reduce congestion.
Conclusion
SVI networking is a powerful solution for optimizing inter-VLAN communication while reducing the dependency on external routers. By implementing SVIs correctly, businesses can achieve better network efficiency, enhanced security, and simplified management. With best practices such as proper IP addressing, security measures, and redundancy planning, organizations can ensure seamless network performance. Understanding and troubleshooting SVI networking issues will further help administrators maintain a robust and efficient network infrastructure.
FAQs About SVI Networking
1. What is SVI networking?
SVI networking refers to the use of Switch Virtual Interfaces to enable inter-VLAN routing on Layer 3 switches, eliminating the need for external routers.
2. How does an SVI differ from a physical router?
An SVI performs routing functions directly on a switch, reducing latency and improving efficiency compared to traditional external routers.
3. What are the advantages of using SVI networking?
It offers faster inter-VLAN routing, simplified network management, reduced hardware requirements, and improved security.
4. Can I configure multiple SVIs on a single switch?
Yes, a single switch can host multiple SVIs, each corresponding to a different VLAN.
5. How do I enable SVI on a Cisco switch?
Use the ip routing command and configure the VLAN interface with an IP address.
6. Why is my SVI not working?
Check if IP routing is enabled, ensure VLANs are correctly assigned, and verify that the VLAN interface is active.
7. Does SVI networking improve security?
Yes, implementing ACLs and VLAN access lists can enhance security by restricting unauthorized access.
8. Can I use SVI networking in small networks?
Yes, SVI networking is beneficial for both small and large networks that require efficient VLAN routing.
9. How can I monitor SVI performance?
Use network monitoring tools like Cisco NetFlow to analyze traffic and optimize performance.
10. What is the difference between SVI and a trunk port?
An SVI is a logical interface for inter-VLAN routing, while a trunk port is a physical port that carries multiple VLANs.